How to boot a Red Hat Enterprise Linux or CentOS
6.x / CentOS 7.x standby virtual machine in an EFI environment
Revised on June 23, 2020
Operating procedures of booting a Red Hat Enterprise Linux or CentOS 6.x / CentOS 7.x
standby virtual machine in an EFI environment
Before booting Red Hat Enterprise Linux or CentOS 6.x / CentOS 7.x standby virtual
machine in an EFI environment, you need to create a boot entry before booting up the standby VM.
The following are the operating procedures how to configure the settings.
ESXi Target Host
- When booting standby VM in EFI environment the
following window is displayed.
Select [Enter Setup] and press Enter key.
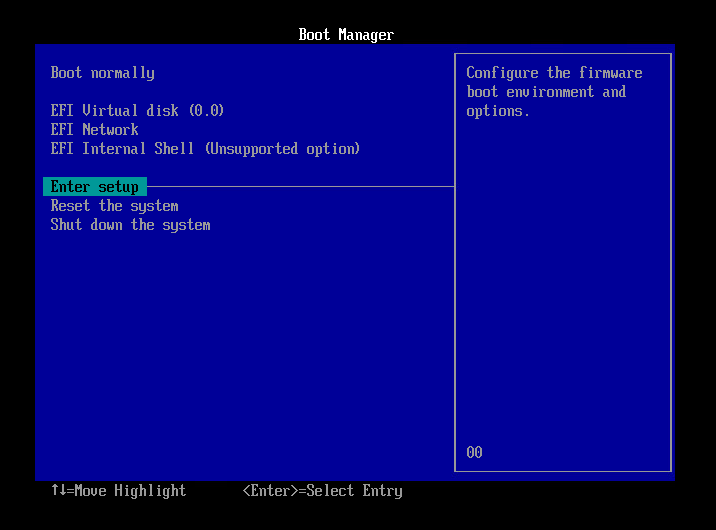
- Select [Configure boot options] and press Enter key.
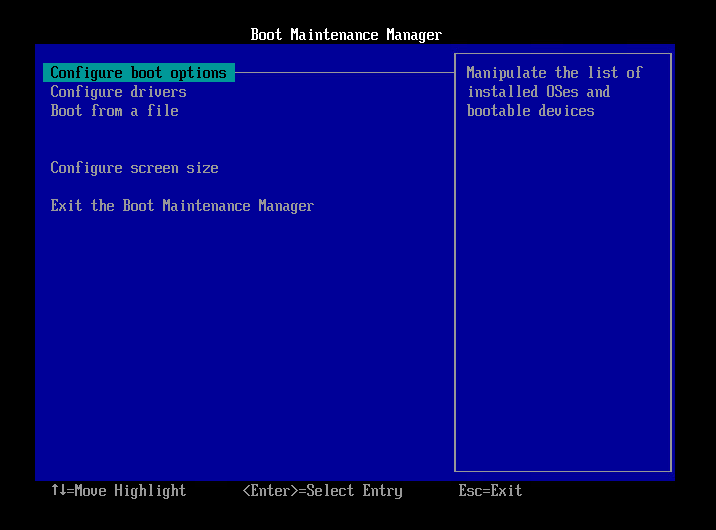
- Select [Add boot option] and press Enter key.
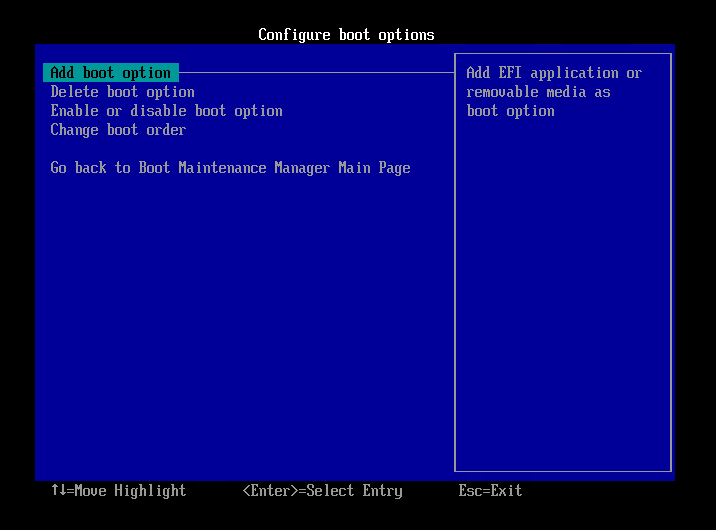
- Select [NO VOLUME LABEL,] and press Enter key.
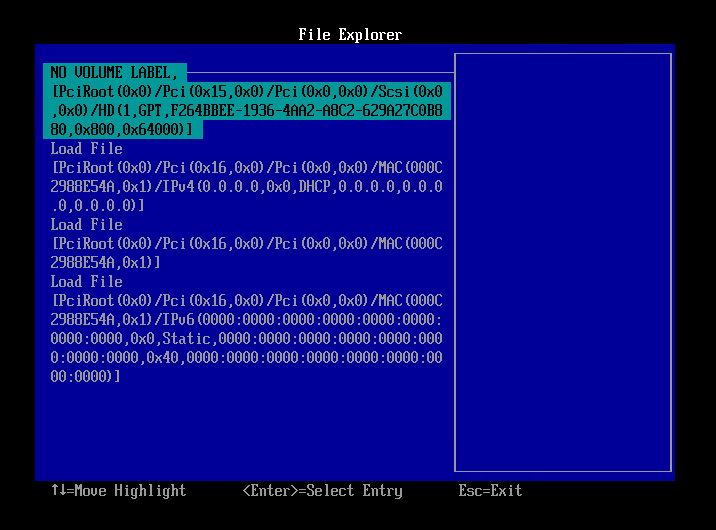
- Select [<EFI>] and press Enter key.
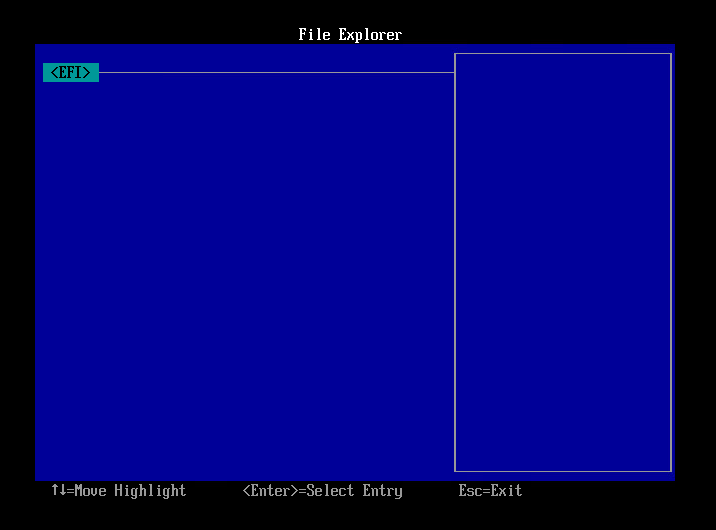
- Select the following and press Enter key.
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux/CentOS 6.x <redhat>
- CentOS 7.x : <centos>
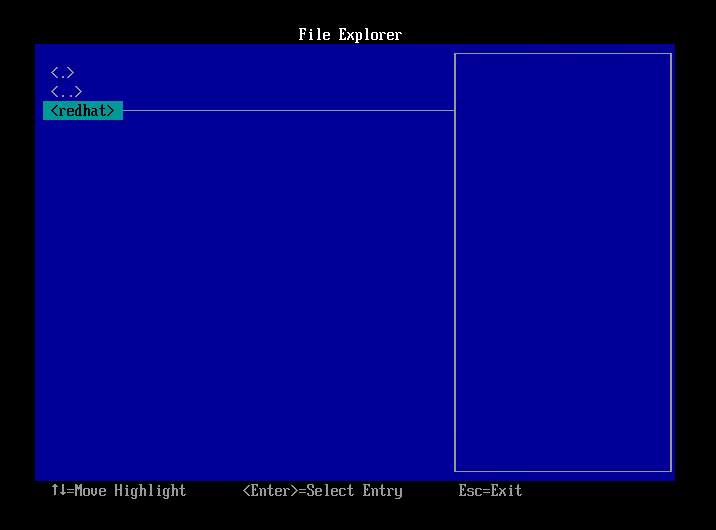
- Select the following and press Enter key.
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux/CentOS 6.x : grub.efi
- CentOS 7.x : shimx64.efi
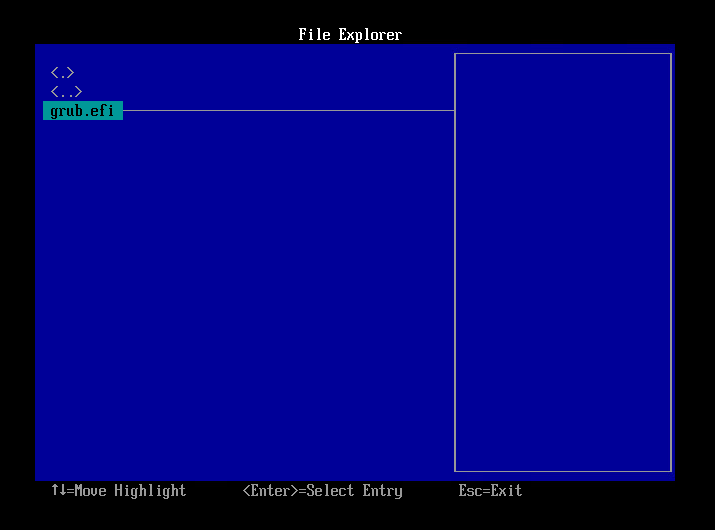
- Select [Input the description] and press Enter key.
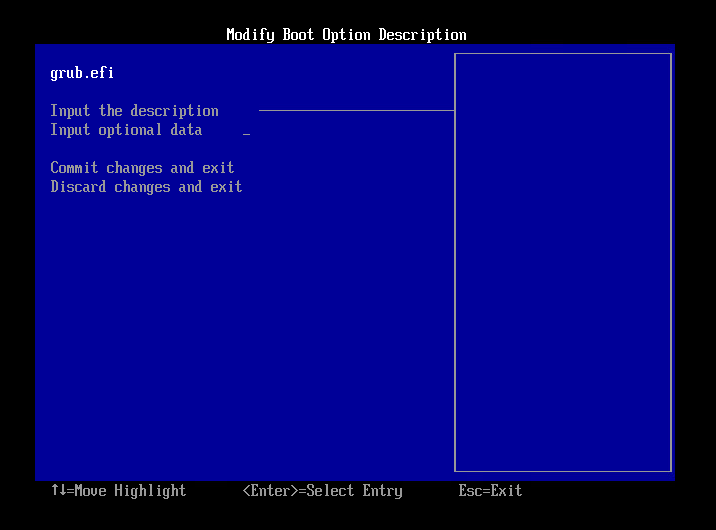
- Enter a label name in the displayed dialog and press Enter key.
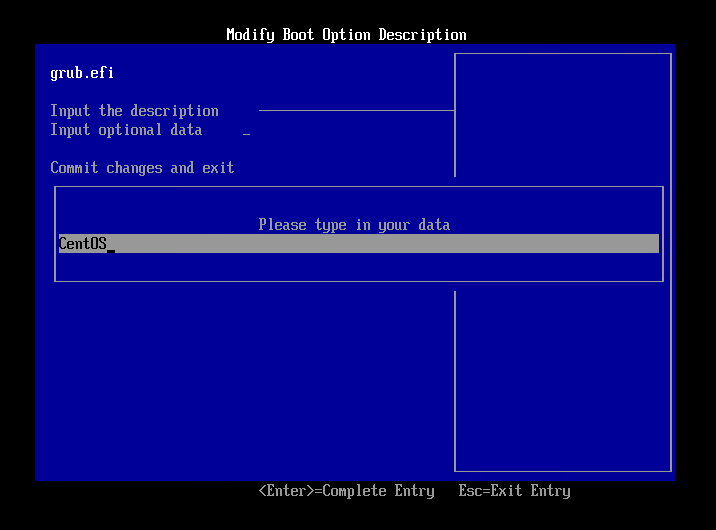
- Select [Commit changes and exit] and press Enter key.
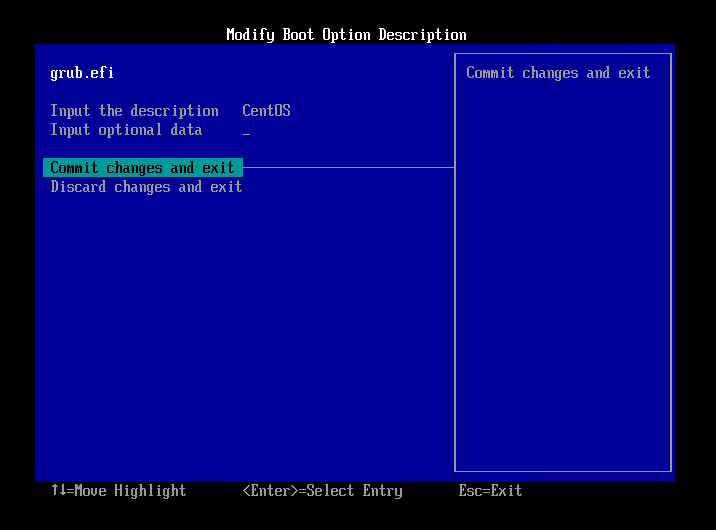
- Select [Exit the Boot Maintenance Manager] and press Enter key.
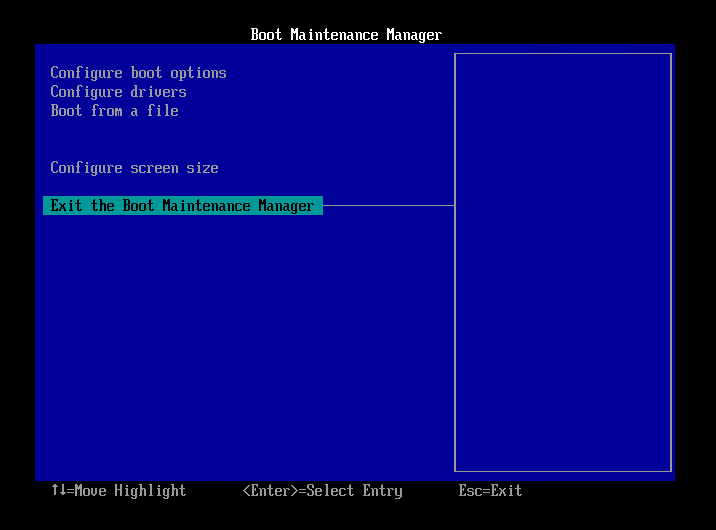
- Select [Shut down the system] and press Enter key.
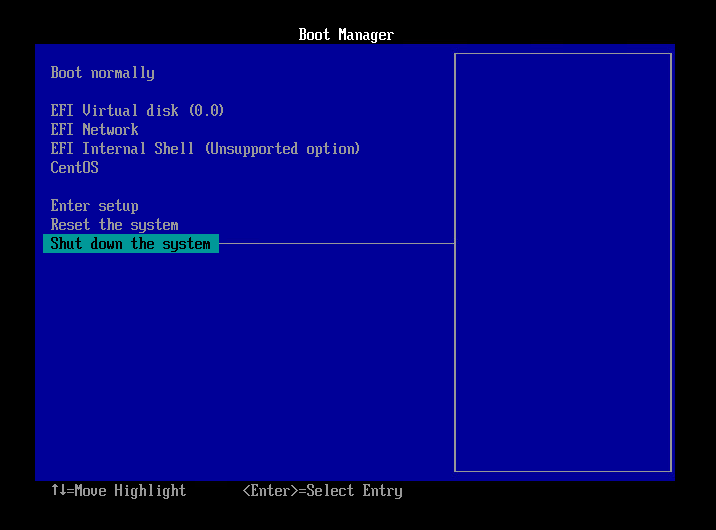
- Now, you can boot up the system.
* When a different boot point (snapshot) is selected, you need to configure the above settings again.
When using ActiveImage Protector CentOSBE
- Boot into CentOSBE and identify the partition the entry is located.
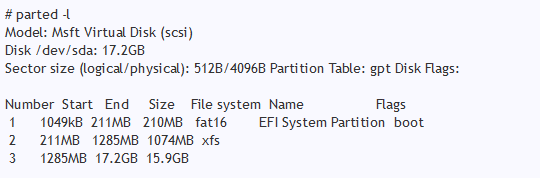 In this example, EFI partition is located in "/dev/sda1".
In this example, EFI partition is located in "/dev/sda1".
- Run the following command and create a boot entry.
CentOS7.5 or earlier
# efibootmgr --create --label CentOS --disk /dev/sda1 --loader /EFI/centos/shimx64.efi
CentOS6.x / RHEL6.x
# efibootmgr --create --label CentOS --disk /dev/sda1 --loader /EFI/redhat/grub.efi
- Boot into CentOSBE again and boot up the OS.
Back to Index


























 In this example, EFI partition is located in "/dev/sda1".
In this example, EFI partition is located in "/dev/sda1".