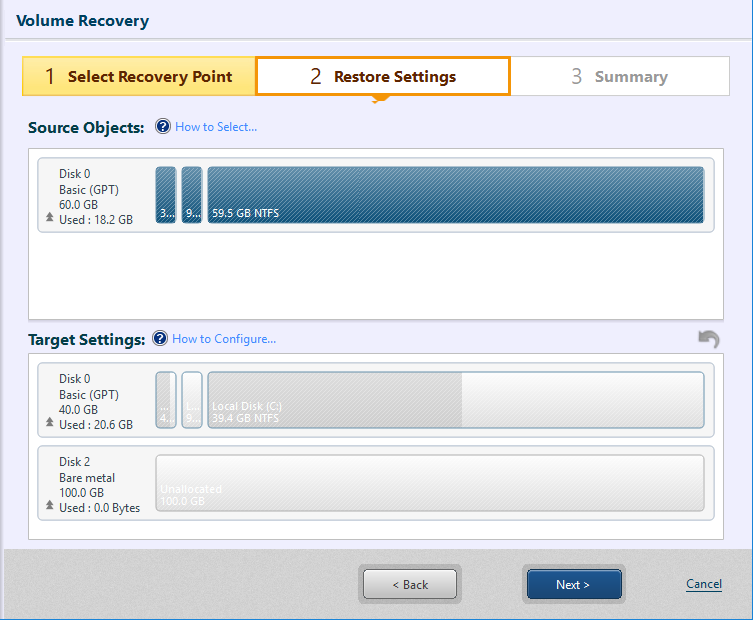
The disk selected with Step 1 is displayed under [Source Objects:]. Drag and drop the item (a disk or a volume) to the restore target disk. You can also right-click on the restore source and select the target.

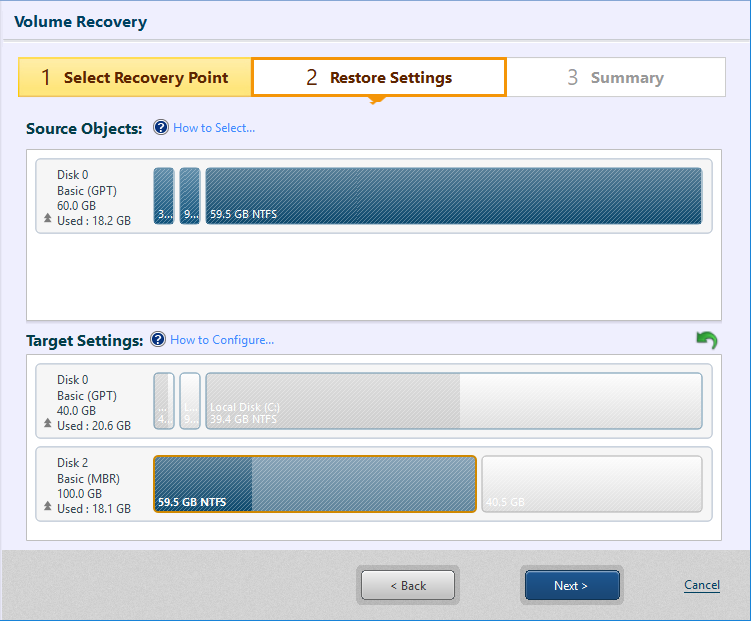
For example, 59.5GB volume displayed in [Source Objects:] is selected to restore to the unallocated space in disk 1 displayed at the bottom of the window.
* When overwriting to restore to an existing volume in a Linux boot environment, please make sure the target volume is unmounted. To unmount the target volume please go to [Utilities] - [Mount (Local)] and select the target volume to unmount.
Right-click on the disk information of the restore target disk and disk restore options are displayed in the menu to restore MBR, First Track, Disk Signature.
Right-click on a volume of the restore target disk and the volume restore options are displayed in the menu to restore drive letter, activate the boot partition, change volume size (to the specified size).
The volume size of the restore target can be adjusted by dragging the right edge of the volume.
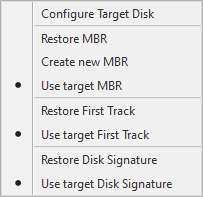
Disk Restore options
|
Item |
Description |
|
MBR |
The MBR (master boot record) is contained in the first sector of the hard disk drive. Master boot record consists of master boot code and partition table. · Restore MBR Select this option to restore the master boot record in the image file. · Create new MBR Select this option to create Windows standard MBR. · Use target MBR The MBR of the destination is used. |
|
First Track |
First track represents the 63 sectors at the beginning of disk drive. ActiveImage Protector excludes the first sector (MBR) and restores the subsequent 62 sectors. As for a disk, first track represents 2048 sectors at the beginning of the disk. ActiveImage Protector excludes the first sector (MBR) and restores the subsequent 2047 sectors. Some boot loader applications require the data to boot up the system. · Restore first track First track of the image file is restored. · Use target First Track First track of the destination is used. |
|
Disk Signature |
Disk signature is used for Windows OS to identify physical disk. · Restore Disk Signature Disk signature of the image file is restored. · Use target disk signature Disk signature of the destination is used. |
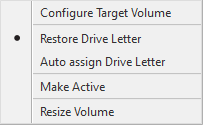
Volume Restore options
|
Item |
Description |
|
Drive Letter |
You can specify how to handle the drive letter assigned to the volume to restore. · Restore Drive Letter The drive letter assigned to the image file is restored. · Auto assign Drive Letter Drive letter is automatically assigned to the restored volume. |
|
Activate boot partition |
· Make Active To restore the boot partition, the partition is activated. |
|
Volume Size |
· Resize Volume If a larger/smaller volume is selected as restore destination, you can select one of the following options to restore the volume in the reduced size or an extended size. For operating procedures of how to restore a volume in reduced size, please refer here. |
Enable [Ignore checksum error] to ignore a checksum error occurred with a backup image and continue the process.
Enable [Post-restore process] to execute the post-restore process upon completion of a restore task.
If restore target disk is bare metal disk, the disk may be initialized. If a restore by volume is performed to a bare metal disk, please make sure that the disk is initialized.
Right-click on the disk information on the disk, context menu is displayed.
* This feature is not provided in Linux boot environment.
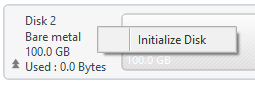
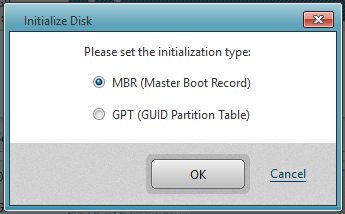
Please select the disk initialization type.
The available space may be partitioned if necessary. Right-click on the space to display the context menu.
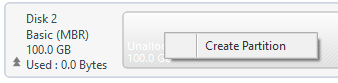
Enter the volume size in [Create Partition] dialog.
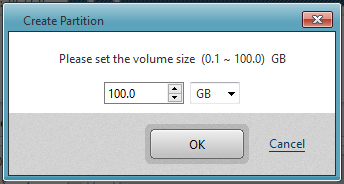
* ActiveImage Protector does not support formatting the created partition.
* Creating partitions by [Create Partition] and overwriting restore to the created partitions cannot be performed by a single task execution.
Click on [Next]